Table partitioning
Breaking the table logically into smaller segments based on some criteria, i.e. the column which we know is going to get used very frequently in where clause.
Partitioning makes the table easy to manage, performance is enhanced.
Advantages
- Improves query performance and is cost-effective
- Increases parallelism
- Independent partitions can be managed indipendently
- Different partitions can live on different filesystems: less frequently accessed data can be placed on slower disks
- Useful while doing upserts on bulk table (for daily incremental loads in datawarehouse)
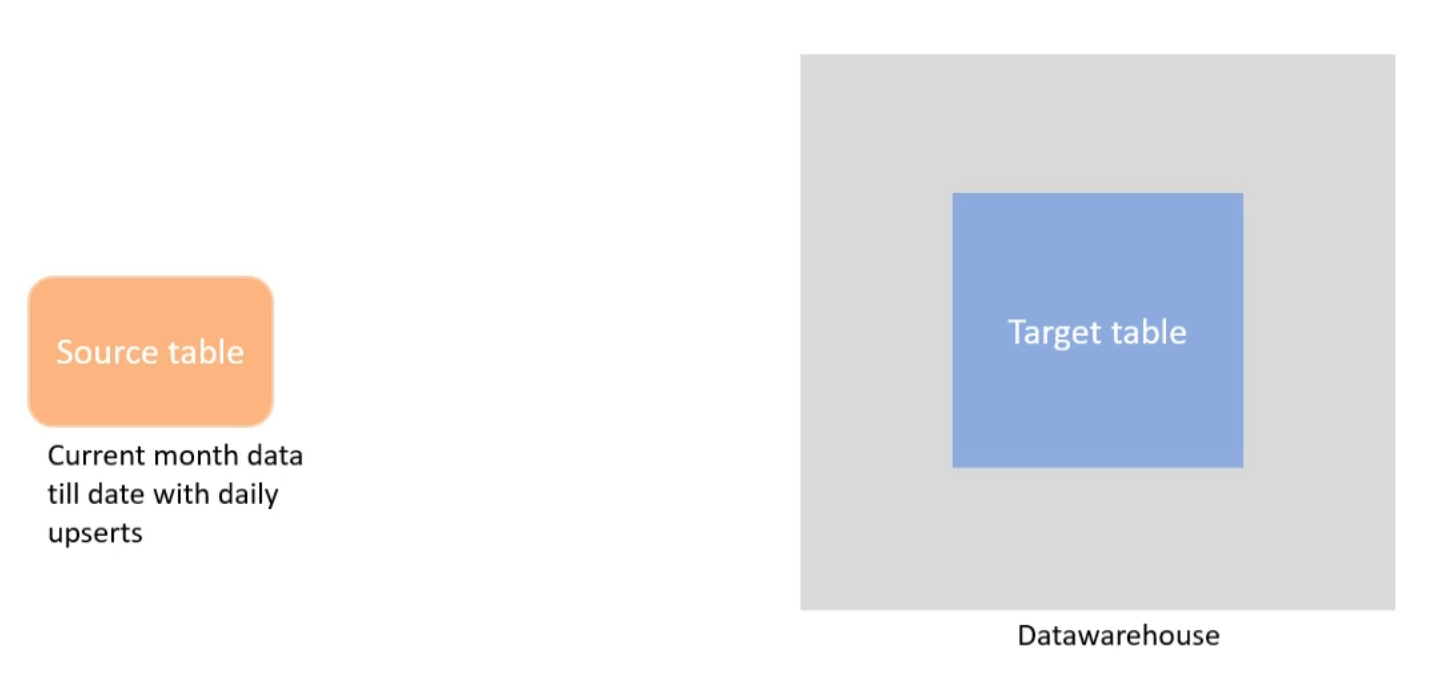
Bulk data example
We have a huge target table in the datawarehouse. It's not partitioned.
The source table is some transactional database containing monthly data and gets refreshed daily with increments.
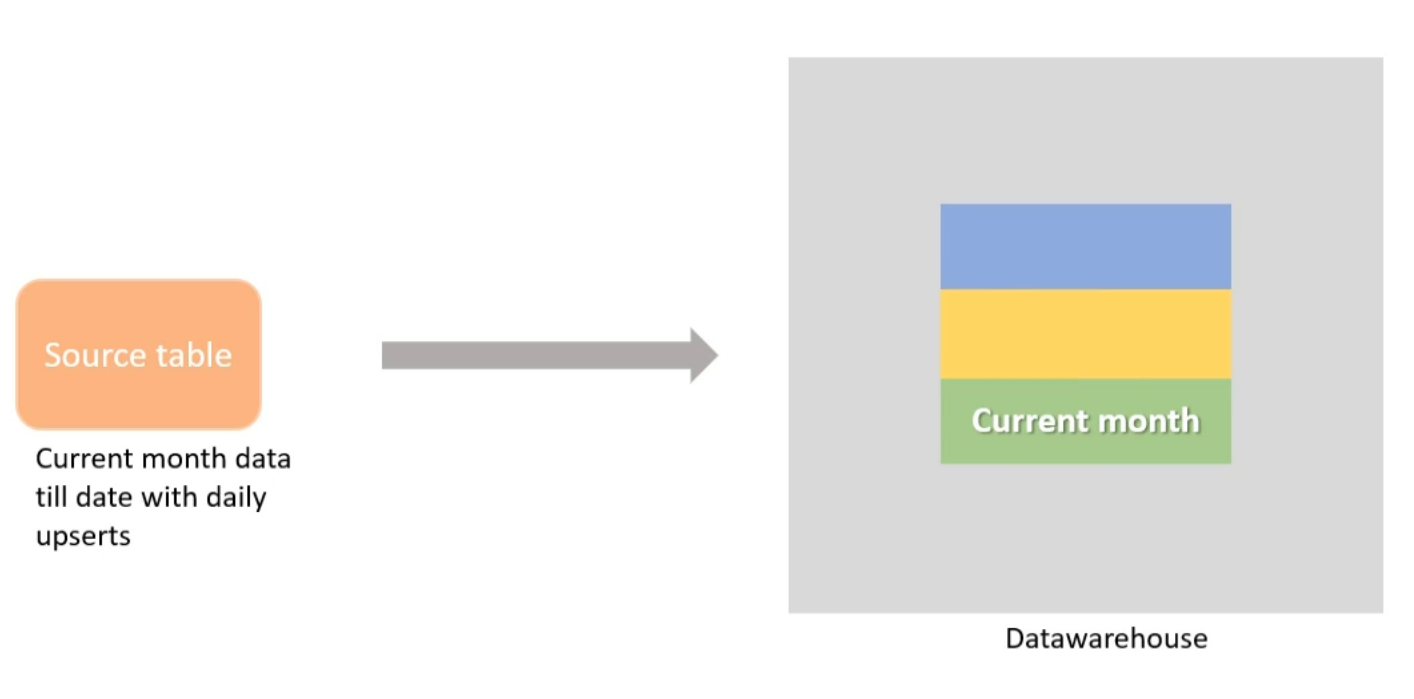
Solution
Partitioning target table on month. And daily switching the partition with a new one from source table.
This takes less time
Creating partitioned table
When creating a table, in Partition and cluster settings, choose between:
- partition by ingestion time (example Ingestion time partition tables)
- or partition by field (example Field partition)
Require partitioning filter (optional)
Users are mandate to include a WHERE clause on the partitioning column qhile they query the table.
This implies that user is forced to take full use of partitioning while the table is partitioned. It may reduce cost and improve performances
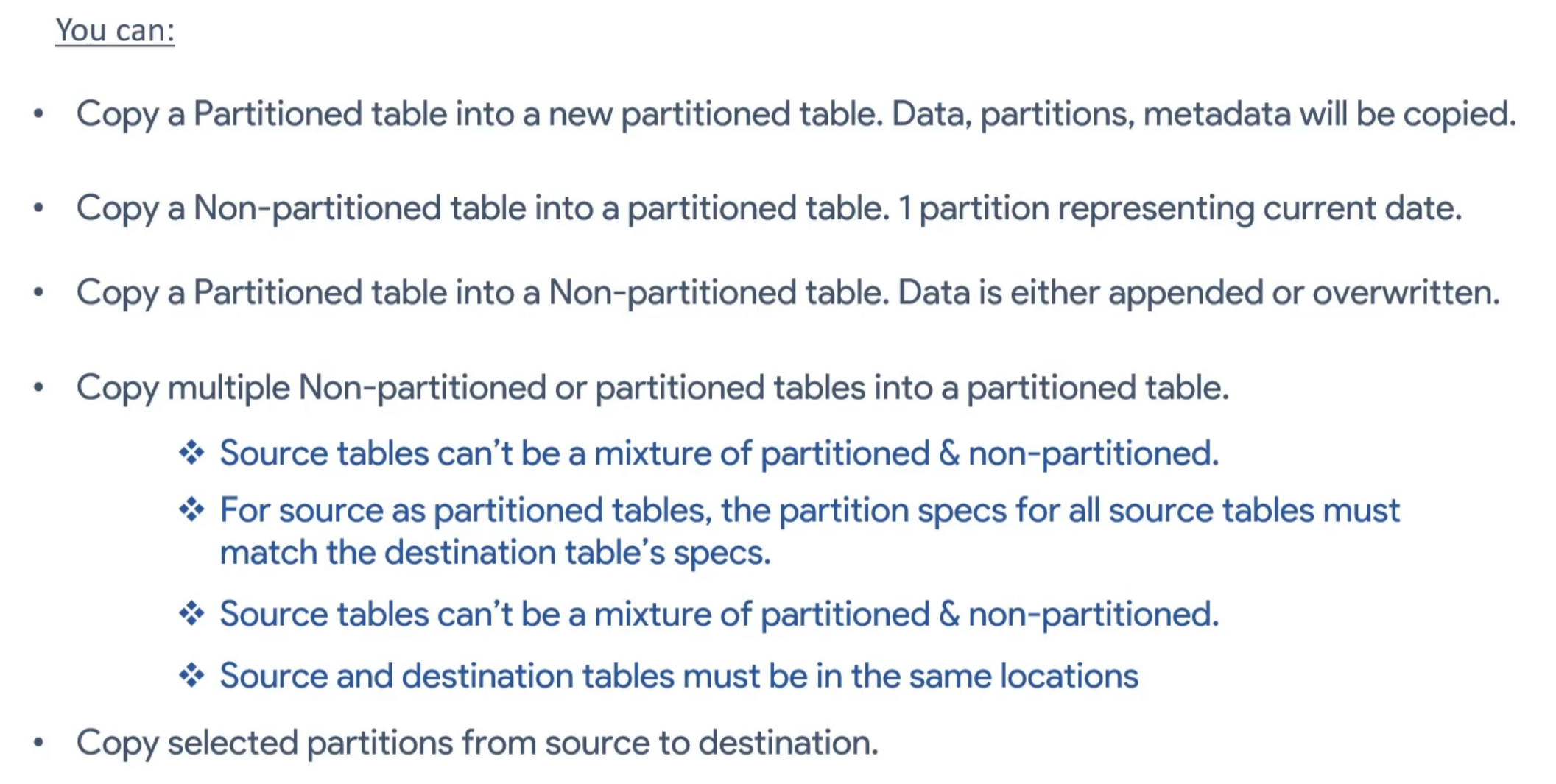
Copy and paste
DML ops
Same as normal but adding a fltering on the partition